퀵 정렬(Quick Sort)
퀵 정렬(Quick Sort) 관련 개념 정리글 입니다.
퀵 정렬(Quick Sort)은 분할 정복(Divide and Conquer) 알고리즘을 기반으로 하는 정렬 알고리즘 중 하나로, 평균적으로 매우 빠른 실행 속도를 가지고 있다.
정의
퀵 정렬(Quick Sort)은 분할 정복(Divide and Conquer) 방법을 사용하여 리스트를 정렬하는 알고리즘이다. 대표적인 비교 정렬 알고리즘 중 하나로, 평균적으로 \(O(nlogn)\)의 시간 복잡도를 가지며, 퀵 정렬의 성능은 피벗(pivot)을 선택하는 방법에 따라 달라진다.
퀵 정렬의 기본 아이디어는 분할 정복 방법이다. 리스트를 두 개의 작은 리스트로 분할하고, 각각을 정렬한 다음, 두 개의 정렬된 리스트를 합하여 전체 리스트가 정렬된 리스트가 되도록 한다.
동작 방식
기준점(Pivot)을 선택한다. 배열의 첫번째 원소, 마지막 원소, 중간 원소 등을 기준으로 선택할 수 있다.
선택한 기준점을 기준으로 배열을 두 개의 부분 배열로 분할한다. 기준점보다 작은 원소는 왼쪽 부분 배열로, 큰 원소는 오른쪽 부분 배열로 분할한다.
왼쪽 부분 배열과 오른쪽 부분 배열에 대해 각각 재귀적으로 퀵 정렬을 수행한다.
부분 배열이 더 이상 분할되지 않으면 정렬이 완료됩니다.
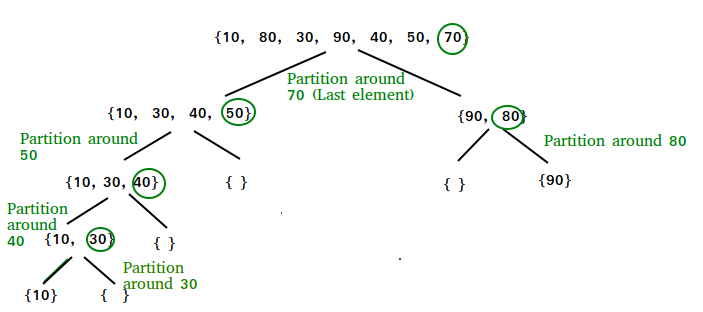
Quick Sort 동작 방식
특징
- 장점
- 문제를 쉽게 풀 수 있게 해주는 분할 정복 알고리즘이다.
- 대용량 데이터 세트에서 효율적이다.
- 작동하는 데 적은 양의 메모리만 필요하므로 오버헤드가 낮다.
- 단점
- 평균적으로 가장 빠른 수행 속도를 가지지만 최악의 경우 시간 복잡도는 \(O(n^{2})\)이다. (pivot이 가장 작은 원소 or 가장 큰 원소일 때)
- 작은 데이터 세트에는 적합하지 않다.
- 불안정 정렬(Unstable Sort)이다.
불안정 정렬 - 정렬된 결과에서 같은 값을 가지는 요소의 순서가 정렬 이전과 동일하게 유지되지 않는 정렬 알고리즘
구현 방법
대표적인 구현 방법은 두가지가 있다.
Lomuto partition scheme
기준점보다 작은 원소를 찾아서 왼쪽으로 옮기고, 큰 원소를 찾아서 오른쪽으로 옮기는 과정을 반복하는 방식이다.
이 방식은 코드가 간결하고 직관적이지만, 원소들이 균등하게 분할되지 않을 가능성이 있다.
''' Python3 implementation QuickSort using Lomuto's partition Scheme.'''
def partition(arr, low, high):
# pivot
pivot = arr[high]
# Index of smaller element
i = (low - 1)
for j in range(low, high):
# If current element is smaller than or
# equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot):
# increment index of smaller element
i += 1
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
arr[i + 1], arr[high] = arr[high], arr[i + 1]
return (i + 1)
''' The main function that implements QuickSort
arr --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index '''
def quickSort(arr, low, high):
if (low < high):
''' pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now at right place '''
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
# Separately sort elements before
# partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1)
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high)
''' Function to print an array '''
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
print()
# Driver code
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
n = len(arr)
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1)
print("Sorted array:")
printArray(arr, n)
#output
# Sorted array:
# 1 5 7 8 9 10
Lomuto partition scheme 코드 예시 (시간 복잡도 \(O(n^{2})\))
Hoare partition scheme
두 개의 인덱스를 사용하여 배열을 분할하는 방식으로, 두 인덱스가 서로 교차할 때까지 반복하여 작은 원소와 큰 원소를 찾아서 서로 교환하는 방식이다.
이 방식은 Lomuto partition scheme보다 더욱 효율적인 분할이 가능하며, 일반적으로 더욱 빠른 수행 속도를 가진다.
''' Python implementation of QuickSort using Hoare's partition scheme. '''
def partition(arr, low, high):
pivot = arr[low]
i = low - 1
j = high + 1
while (True):
# Find leftmost element greater than
# or equal to pivot
i += 1
while (arr[i] < pivot):
i += 1
# Find rightmost element smaller than
# or equal to pivot
j -= 1
while (arr[j] > pivot):
j -= 1
# If two pointers met.
if (i >= j):
return j
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
''' The main function that implements QuickSort
arr --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index '''
def quickSort(arr, low, high):
''' pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now at right place '''
if (low < high):
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
# Separately sort elements before
# partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi)
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high)
''' Function to print an array '''
def printArray(arr, n):
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
print()
# Driver code
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
n = len(arr)
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1)
print("Sorted array:")
printArray(arr, n)
#output
# Sorted array:
# 1 5 7 8 9 10
Hoare partition scheme 예시 코드 (시간 복잡도 \(O(n)\))
결론
퀵 정렬은 평균 시간복잡도가 \(O(nlogn)\)인 빠르고 효율적인 정렬 알고리즘이라고 할 수 있다.
원래 문제를 해결하기 더 쉬운 더 작은 하위 문제로 분해하는 분할 정복 알고리즘이다.
반복 및 재귀 형식으로 쉽게 구현할 수 있으며 대규모 데이터 세트에서 효율적이며 데이터를 제자리에서 정렬하는 데 사용할 수 있다.
피벗이 잘못 선택되었을 때 발생하는 \(O(n^{2})\) 의 최악의 경우 시간 복잡도와 같은 몇 가지 단점도 있다. (퀵 정렬의 성능은 피벗 선택에 민감하다)
참고 문헌 및 사이트
광운대학교 박재성 교수님의 자료구조 강의 자료
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/hoares-vs-lomuto-partition-scheme-quicksort/
chat gpt
